In the digital age, computer software applications are indispensable tools that empower users to accomplish a wide variety of tasks. Whether it’s managing data, creating content, or automating processes, understanding the various types of software and their applications is essential for anyone navigating today’s technology-driven landscape. This article delves into the types, features, and benefits of computer software applications, filling gaps often found in competing resources.
What Are Computer Software Applications?
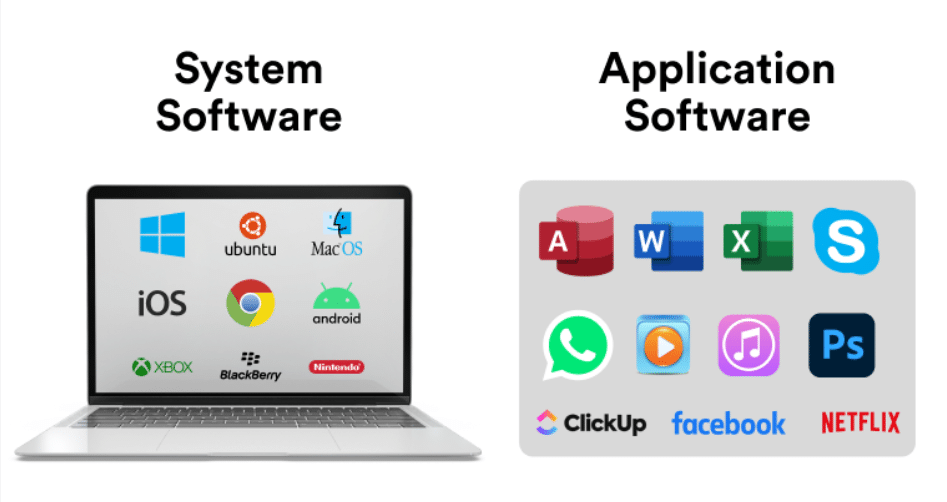
Computer software applications are programs designed to perform specific tasks for users. They work in tandem with system software, which manages the hardware and foundational functions of a computer. Broadly speaking, software applications can be divided into two categories:
- System Software: The backbone that enables hardware and software to work together.
- Application Software: Tools for end-users to execute specialized tasks.
Categories of Software Applications
1. System Software
System software acts as the bridge between the hardware and application software. It ensures smooth operation by managing resources and system functionality. Key components include:
- Operating Systems (OS):
These manage hardware and software resources, ensuring seamless user interaction.
Examples: Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android. - Device Drivers:
Software that enables the operating system to communicate with hardware devices.
Examples: Printer drivers, graphic card drivers, and audio drivers. - Firmware:
Built-in software embedded in hardware devices to control basic operations.
Examples: BIOS, UEFI, and firmware in smart appliances. - Utility Programs:
Maintenance tools that optimize system performance.
Examples: Disk Cleanup, antivirus software, and backup utilities.
Missed Gap in Competitor’s Article
Most competitors overlook advanced utility software like file recovery tools or diagnostic utilities, which are crucial for maintaining system health.
2. Application Software
Application software is developed to help users accomplish specific tasks efficiently. Common categories include:
- Productivity Software:
Tools for document creation, data analysis, and project management.
Examples: Microsoft Office Suite, Google Workspace, and Trello. - Multimedia Software:
Used for creating, editing, and consuming multimedia content.
Examples: Adobe Photoshop, VLC Media Player, and Final Cut Pro. - Educational Software:
Programs designed to facilitate learning and skill development.
Examples: Duolingo, MATLAB, and educational games. - Web Browsers:
Applications for accessing the internet.
Examples: Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari. - Business Software:
Applications tailored for business operations like accounting and inventory management.
Examples: QuickBooks, Salesforce, and SAP.
Enhancement Idea:
In addition to these categories, highlighting industry-specific software (e.g., architectural design tools like AutoCAD or medical software like EPIC Systems) could set this guide apart.
Key Features of Modern Software Applications
Software applications today come equipped with robust features that enhance usability and efficiency. Here are some notable aspects:
- Cloud Integration:
Enables data storage and access across devices through platforms like Google Drive and Dropbox. - User-Friendly Interfaces:
Intuitive designs that make software accessible to all user levels. - Cross-Platform Compatibility:
Software operable on multiple operating systems, ensuring flexibility for users. - Automation Capabilities:
Features like automated workflows in tools such as Zapier enhance productivity.
Comparison of Popular Software Applications
| Category | Example Software | Primary Use | Distinct Feature |
| Operating Systems | Windows, macOS | System management | Comprehensive support for hardware |
| Productivity Tools | Microsoft Excel | Data analysis | Advanced pivot table functionality |
| Multimedia Software | Adobe Premiere Pro | Video editing | Professional-grade editing tools |
| Educational Software | Khan Academy | Learning and development | Free courses for diverse subjects |
| Business Software | Salesforce | Customer relationship management (CRM) | AI-driven sales analytics |
Choosing the Right Software: Key Considerations
When selecting a software application, consider the following factors:
- Purpose:
Define the primary task you aim to accomplish. - Cost:
Assess the total cost, including licenses and subscriptions. - System Requirements:
Ensure compatibility with your device specifications. - Reviews and Ratings:
Rely on user feedback to gauge performance and reliability.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Computer software applications play a pivotal role in personal and professional domains. By understanding the various types, features, and examples, users can make informed decisions that align with their goals. Whether you’re a student, a business professional, or a casual user, choosing the right tools will significantly enhance your productivity and efficiency.
For those interested in diving deeper into specific software categories, explore detailed guides or seek professional advice to tailor your choices.

